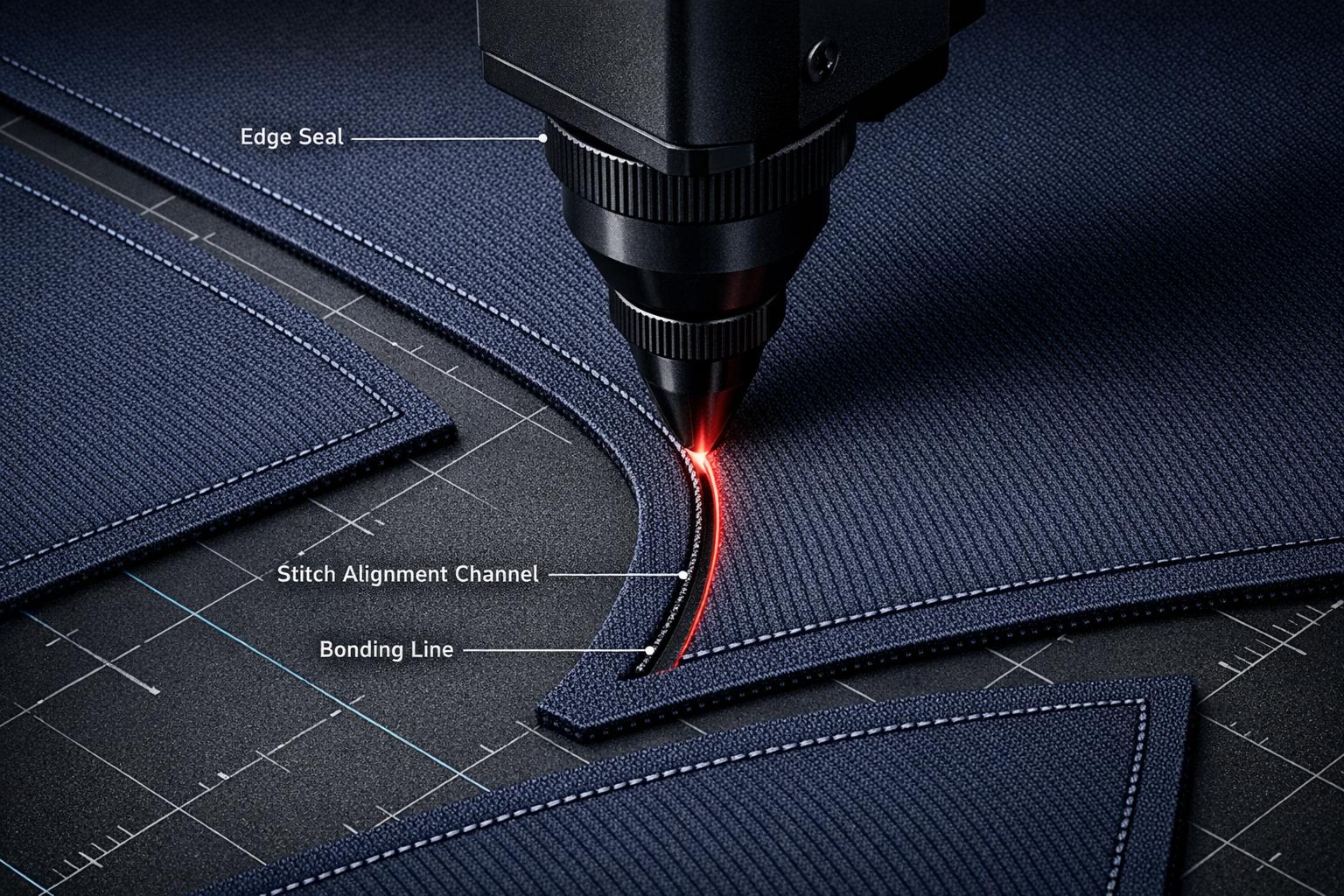
Laser cutting transforms fabric processing by delivering unmatched accuracy and clean finishes. Unlike traditional cutting tools, lasers use a focused beam of light to cut fabrics without physical contact, ensuring edges are sealed to prevent fraying. Here’s why this matters:
- Precision: Achieves tolerances as tight as ±0.1 mm, critical for activewear fit and performance.
- Durability: Sealed edges withstand stretching and washing, prolonging garment lifespan.
- Efficiency: CAD-guided automation reduces material waste by 15% and eliminates rework.
- Complex Designs: Handles intricate patterns and ventilation features with ease.
How Laser Cutting Works for Fabric
The Mechanics of Laser Cutting
Laser cutting for fabric starts with a focused beam of energy, typically from a CO₂ laser, which is widely used for cutting activewear materials. The laser beam is amplified and directed through mirrors into a cutting head, where a lens concentrates it into a fine spot, usually between 0.1–0.3 mm in diameter.
When the laser hits the fabric, it generates intense heat – ranging from 572°F to 932°F (300–500°C) – that either vaporizes or melts the fibers along the cutting line. For synthetic fabrics, this heat fuses the fibers at the edges, creating a sealed finish that prevents fraying, eliminating the need for extra edge treatments. Since the process is non-contact, there’s no physical force applied to the material, which avoids issues like stretching or distortion.
To achieve precise cuts with minimal waste, settings like power, speed, focus, and air assist need to be carefully balanced. For instance, cutting polyester often requires medium power (60–100W), speeds of 6.5–10 feet per minute (2–3 m/min), and high air pressure (1.5–2 Bar) to remove molten material quickly and prevent buildup along the edges. This level of precision ensures narrow kerfs – typically between 0.004–0.02 inches – and supports efficient material use.
Automation and Efficiency in Laser Cutting
Modern laser cutting systems take precision to the next level by incorporating CNC automation. Designers first create patterns in CAD software, which are then translated into G-code instructions. These commands guide the laser head with pinpoint accuracy, allowing it to maintain cutting tolerances of around ±0.003 inches (±0.075 mm).
Some advanced systems also use vision-guided technology, employing CCD cameras to monitor the cutting process in real-time. These cameras can detect printed patterns on the fabric and adjust the cutting path automatically to correct for distortions or misalignments. In addition, some setups feature AI algorithms that analyze the quality of the cuts during operation, making on-the-fly adjustments to power and speed settings for consistently optimal results.
These innovations make laser cutting not only precise but also incredibly efficient. Automatic single-ply laser cutters can reach speeds of 98 to 131 feet per minute (30–40 m/min), far outpacing traditional multi-ply knife cutters. This combination of speed and precision is essential for working with high-performance fabrics.
sbb-itb-8dbc09a
Fabric Cutting Machine | CO2 Laser vs Scissor
Benefits of Laser Cutting vs. Traditional Cutting Methods
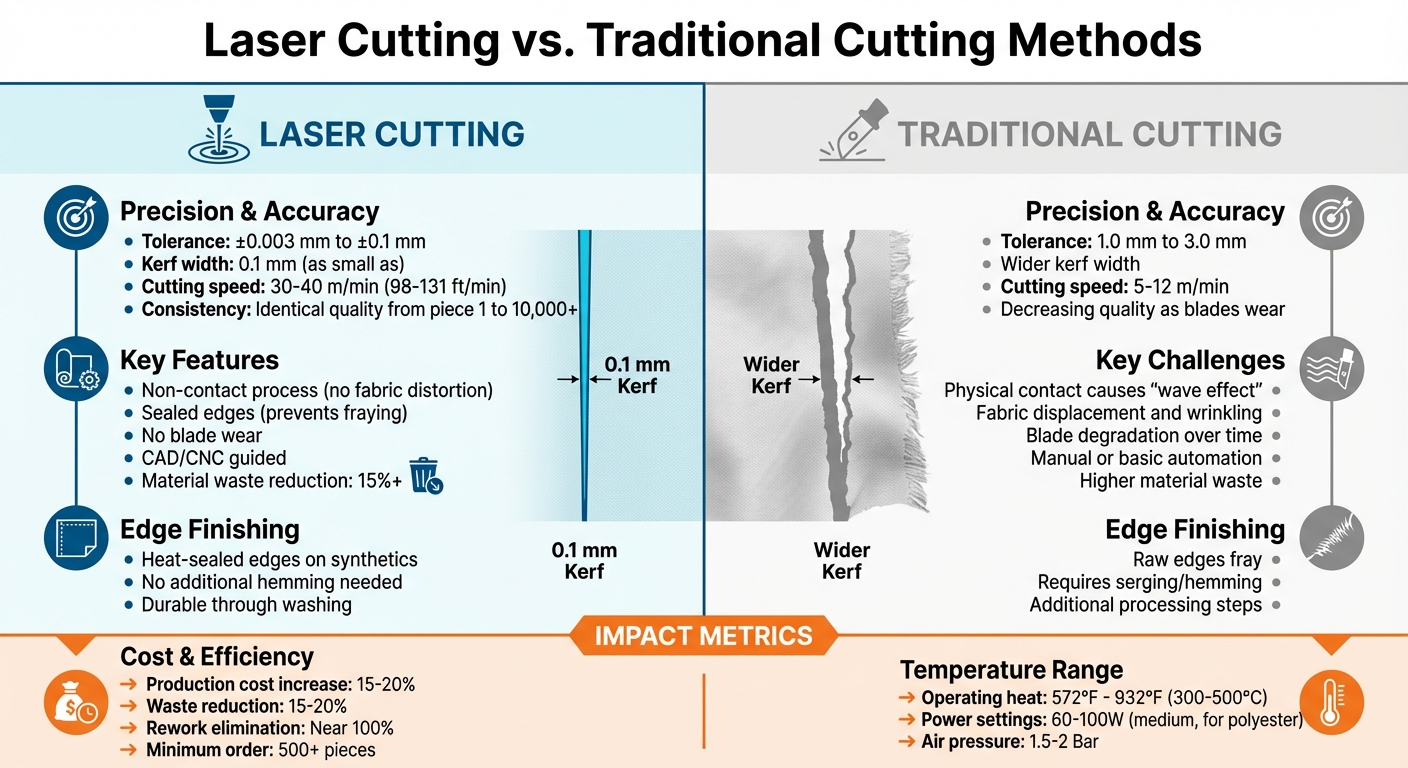
Laser Cutting vs Traditional Cutting Methods for Fabric: Precision and Efficiency Comparison
Laser cutting stands out for its precision and efficiency, offering several advantages over traditional cutting techniques.
Accuracy and Consistency
Traditional cutting tools, like blades, often cause issues such as fabric displacement, wrinkling, or pulling – especially with delicate materials. Laser cutting eliminates these problems because the beam never physically touches the fabric.
With tolerances ranging from ±0.003 mm to ±0.1 mm, laser cutting is far more precise than mechanical methods, which typically achieve tolerances between 1.0 mm and 3.0 mm. This level of accuracy remains consistent throughout production, unlike blades that wear down over time.
Additionally, the narrow kerf width – sometimes as small as 0.1 mm – enables tighter nesting of patterns, reducing fabric waste by over 15%. Because laser systems use CAD software and CNC controls, even the most intricate designs can be replicated perfectly across multiple production runs.
This combination of precision and consistency also lays the groundwork for superior edge finishing.
Sealed Edge Finishing
One of the standout features of laser cutting is its ability to seal edges on synthetic fabrics. The laser’s heat melts and fuses fibers as it cuts, preventing fraying. This eliminates the need for additional finishing steps like serging or hemming, which simplifies the manufacturing process. It can also enhance the durability of products, ensuring they withstand repeated washing and wear.
But the benefits don’t stop at precision and edge sealing – laser cutting also excels in handling intricate and complex designs.
Flexibility for Complex Designs
Laser cutting is ideal for intricate patterns that traditional methods struggle to handle. Features like sharp internal corners, tiny perforations, and hollow patterns can be executed with ease, thanks to the laser’s small spot size, typically ranging from 0.1 mm to 0.3 mm. Traditional tools like knife molds and die cutters often require custom tooling to achieve similar results, and even then, they can’t match the precision of a laser.
The digital workflow of laser cutting further enhances its flexibility. Designers can go straight from concept to production without needing physical templates or costly metal dies. This makes laser cutting especially useful for custom designs, rapid prototyping, and small-batch production.
"A laser’s focused beam can navigate these complex geometries effortlessly, producing sharp, clean results that are impossible to achieve manually." – RedShift Laser
Applications of Laser Cutting in Activewear
Laser cutting has become a game-changer in the activewear industry, addressing challenges that traditional methods often face. Whether it’s achieving precision on stretchy fabrics or incorporating intricate ventilation designs, this technology ensures reliable, high-quality results for performance-focused apparel. Let’s dive into how laser cutting handles various fabric challenges with ease.
Cutting Stretchable Fabrics with Precision
Stretchable fabrics like spandex, Lycra, and polyester blends are notoriously tricky to handle with conventional cutting tools. These materials tend to shift and distort, leading to inaccuracies. Laser cutting solves this problem with its non-contact processing, eliminating the "wave effect" caused by physical tools.
"Fabric is alive, it moves, and when a tool touches it, it tends to create a wave that moves forward with the tool. This will create inaccuracy in the cut." – Christina Lefebvre, Area Sales Manager, North America, Matic
The laser’s heat not only cuts but also seals the edges of synthetic fibers, preventing fraying and removing the need for extra hemming . For elastic materials, manufacturers account for a slight thermal shrinkage of 0.1–0.3 mm during the design stage. Modern CO₂ lasers offer cutting accuracy within ±0.1 mm and operate significantly faster – 30–40 m/min compared to the 5–12 m/min speeds of traditional automatic knife cutters .
Creating Ventilation Features and Perforations
Laser cutting shines when it comes to adding ventilation features to activewear. Precise perforations are crucial for improving breathability, especially in garments designed for running or outdoor activities. Lasers can produce intricate hollow patterns and tiny holes that mechanical blades struggle to achieve without snagging or distorting the fabric .
Additionally, laser cutting minimizes material waste through optimized, mirror-symmetry layouts, reducing waste by 15–20%. Compressed air is used during the process to blow away debris, ensuring clean, unburnt edges.
Custom Patterns and Branding
Laser technology offers unparalleled opportunities for customization, both functional and aesthetic. Designers can create complex lace-like patterns, curved edges, and hollow cut-outs that are impossible to replicate with traditional die-cutting methods. Using CAD software, patterns can be adjusted instantly without the need to create new physical dies .
These intricate designs not only enhance the garment’s appearance but also provide anti-counterfeiting advantages, as they’re difficult for competitors to duplicate. However, this level of precision often increases production costs by 15–20% and usually requires minimum order quantities of 500 or more pieces. For synthetic materials like polyester and nylon blends, manufacturers rely on medium power settings (60–100W) and high air pressure (1.5–2 Bar) to quickly remove molten material and avoid residue buildup. This level of detail ensures consistent quality across all activewear pieces.
How Laser Cutting Reduces Manufacturing Errors
Manufacturing defects can be costly. Every poorly aligned seam, frayed edge, or uneven cut leads to wasted materials and delays. Laser cutting tackles these problems by eliminating the physical contact that often causes errors in traditional methods. Its non-contact design directly addresses many of the flaws seen with conventional cutting tools.
Preventing Common Manufacturing Defects
Traditional cutting tools, like blades and knives, can distort lightweight or stretchable fabrics, leading to misalignment and inconsistent sizing. Laser cutting, on the other hand, uses a thermal process that avoids these issues entirely .
"The conventional cutting tools such as band blades, discs and reciprocating knives suffer from the limitations especially on delicate materials as the cutting force can displace the material, which can lead to inaccurate cutting."
– R. Nayak and R. Padhye, Fashion and Textiles
For materials like those used in activewear, the heat from the laser seals the edges as it cuts, preventing fraying and removing the need for additional hemming steps.
Another advantage is that lasers don’t wear down like traditional blades. This means the cutting quality stays consistent throughout the entire production process, whether it’s the first item or the 10,000th.
Precision is another strong suit of laser cutting. Computer-guided systems ensure accuracy down to ±0.1 mm, making it possible to cut intricate patterns and fine details with ease .
Reducing the Need for Rework
Because laser cutting creates precise, consistent cuts, the need for rework is dramatically reduced. With sealed edges and no fraying, there’s no need for additional steps like manual edge finishing or trimming loose threads, which speeds up production .
In July 2024, researchers used an artificial neural network (ANN) model to optimize laser parameters over 10,000 iterations. This breakthrough allowed for near-perfect predictive accuracy, eliminating trial-and-error processes and ensuring flawless cuts with no need for rework.
Digital integration adds another layer of precision. CAD/CNC software sends designs directly to the laser, minimizing human error in pattern placement. Smart nesting software further reduces material waste by optimizing pattern layouts, cutting fabric usage by 15% or more and lowering overall production costs.
Conclusion
Laser cutting has redefined activewear manufacturing by delivering unmatched precision and efficiency. With accuracy often reaching ±0.1 mm, this technology prevents distortion through its non-contact process and seals fabric edges to eliminate fraying. These features not only reduce errors but also ensure the durability and performance that activewear consumers expect. This approach effectively addresses the challenges of working with delicate, stretchable materials that traditional blades often fail to process without compromising quality.
Beyond its clean cuts, laser cutting ensures exceptional consistency – every piece, from the first to the 10,000th, is identical. The integration of CAD/CNC systems minimizes placement errors, while advanced nesting software can cut fabric waste by 15% or more. Together, these advancements lead to higher-quality garments with fewer defects and less material waste.
The industry recognizes these benefits:
"A CO₂ laser cutter delivers high-speed, millimeter-level precision, and perfectly sealed edges. This technology eliminates fabric distortion and fraying, ensuring consistent quality for both small custom batches and large-scale production runs."
– RedShift Laser
For activewear production, where precision and durability are non-negotiable, laser cutting offers the flexibility needed to create complex patterns, ventilation designs, and intricate details that traditional methods simply can’t achieve. While it may increase production costs by 15–20%, the reduction in defects, rework, and waste makes it a worthwhile investment. This shift toward laser cutting represents a major leap forward in fabric processing, enabling the creation of better-fitting, longer-lasting activewear that meets the high expectations of today’s performance-driven consumers.
FAQs
Which fabrics work best with laser cutting?
Natural fabrics – like cotton, silk, linen, and denim – are excellent choices for laser cutting because they tend to create clean edges and intricate designs with ease. Synthetic options, such as polyester, are also effective, as the laser’s controlled heat helps seal the edges, preventing fraying. That said, fine-tuning the laser settings is key, especially for delicate fabrics, to minimize problems like carbonization. Among all materials, natural textiles generally provide the most reliable outcomes.
Will laser cutting damage or discolor fabric?
Laser cutting can sometimes leave burn marks or discoloration on materials if not handled properly. But with the right techniques and precise adjustments to the settings, these problems can be minimized – or even prevented entirely – keeping the fabric clean and undamaged.
What file format do I need for CAD-to-laser cutting?
For CAD-to-laser cutting, it’s best to use vector file formats such as DXF or DWG. These formats are specifically designed to work seamlessly with laser cutting machines, ensuring they can handle the precision and detail needed for accurate cuts.